How To Become A Veterinarian
What Is a Veterinarian and What Do They Do?

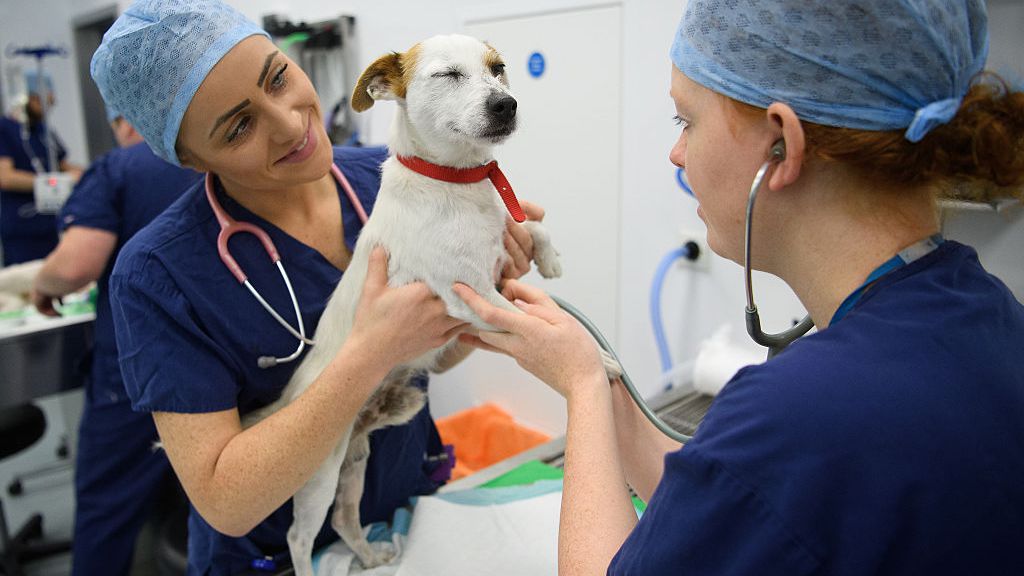
By definition, a veterinarian is a doctor who is qualified to practice the science of prevention, cure, and alleviation of disease and injury in animals. Veterinarians work to diagnose, treat, and research medical conditions of pets, livestock, and other animals. Put another way: if it has wings, a tail, or scales, there’s probably a vet whose job it is to keep it happy and healthy.
Veterinarian Salary
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual salary for veterinarians in May 2019 was $95,460. Veterinarians have a similar median salary to nurse practitioners, and becoming a veterinarian is considered a lucrative employment option in the medical field.
What Are Your Job Prospects as a Veterinarian?
The BLS reports that the veterinary industry is growing much faster than the average growth rate of all industries in the United States. While most jobs are projected to grow by seven percent between 2016 and 2026, veterinary jobs are expected to grow by 19 percent during this same window.
These statistics indicate that it’s a great time to become a veterinarian. Even if you start on your career path today, there will be far more jobs open when you’re done in eight years than there will be in other disciplines. In 2016, there were only 79,600 veterinary jobs in the United States, but in 2026, there will be 94,600.
How Do You Find Work as a Veterinarian?

The contacts you make during your studies will play a key role in your ability to find a job once you graduate. During your clinical studies, you’ll meet a lot of veterinarians who already work in the field, and some of them might work in large companies that are seeking to add more human assets.
Even if you decide to open your own practice immediately after graduating, knowing people in the field will help you with professional networking and support. Knowing the colleagues you will interact with at conferences before you graduate will be a huge plus. If you’re unable to start your own practice and none of your contacts pan out, you can always apply for open veterinary positions in your area.
What Skills Do You Need to Have?

To be a successful veterinarian, you’ll need to have a passion for helping animals live better and happier lives. You should have a general interest in medicine and healing, and you should also have a scientific, analytical mindset that allows you to incorporate lots of information. There are a variety of skills you’ll hone along your path to becoming a full-fledged veterinarian, but here are a few of the core disciplines you’ll need to start honing now if you want to pursue veterinary medicine in the future:
1. Anatomy
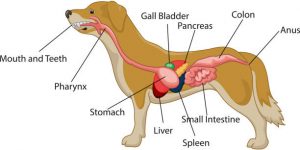
An understanding of basic animal anatomy is essential to becoming a successful veterinarian. During high school, it might be hard to find courses focusing specifically on animal anatomy, but as soon as you start pursuing your undergraduate degree, you’ll gain access to animal anatomy courses that aspiring veterinarians just like you will be taking to hone their skills.
2. Biology

The more you understand about biology, the better you’ll be able to pursue your career path as a veterinarian. A vet’s day-to-day professional life focuses more on animal behavior and common animal maladies, but understanding the core principles of biology will prepare you for the specialized studies you’ll need to undertake as part of your career path.
3. Animal Behavior

Understanding how animals behave is one of the core aspects of being a veterinarian. Since animals can’t speak and tell us what’s wrong, veterinarians need to learn how to recognize the non-verbal cues animals provide that can relate information on their symptoms and underlying conditions.
What Degree Do You Need?

To become a full-fledged veterinarian, you’ll need to complete a four-year undergraduate degree and earn a Doctor of Veterinary Medicine degree. This degree is commonly abbreviated as a DVM or a VMD, and it takes four years to earn.
In some cases, a DVM program might accept applicants who haven’t completed their undergraduate degrees. To be eligible for one of these special programs, you must pursue veterinary-related courses during the first two or three years of your undergraduate studies. Once you’ve entered your DVM program, you’ll study subjects including: Veterinary practice
- Animal health and disease
- Veterinary psychology
- Gross anatomy
- Radiology
- Parasitology
- Pharmacology
Do You Need Any Certifications or Licenses?

Veterinarians everywhere in the United States must be licensed to practice legally. You can only acquire your veterinary license after you have completed an accredited DVM program, and you’ll also have to pass a certification exam. A variety of entities provide certification exams for aspiring veterinarians, but the North American Veterinary Licensing Examination (NAVLE) is considered to be the best exam for easy certification.







