Course Progress Bar
0% Complete
0/43 Steps
Course Navigation
Return to HSE LEVEL 1,2 AND 3 COURSE
Implementing controls to mitigate hazards
Implementing controls to mitigate hazards effectively involves a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and addressing risks in the workplace. Here are steps and strategies for implementing hazard controls:
1. Identify Hazards:
- Conduct a thorough hazard assessment. This involves identifying potential hazards in the workplace, including physical, chemical, biological, ergonomic, and psychosocial hazards.
2. Assess Risk:
- Determine the severity and likelihood of each identified hazard. This risk assessment helps prioritize which hazards require immediate attention.
3. Select Appropriate Controls:
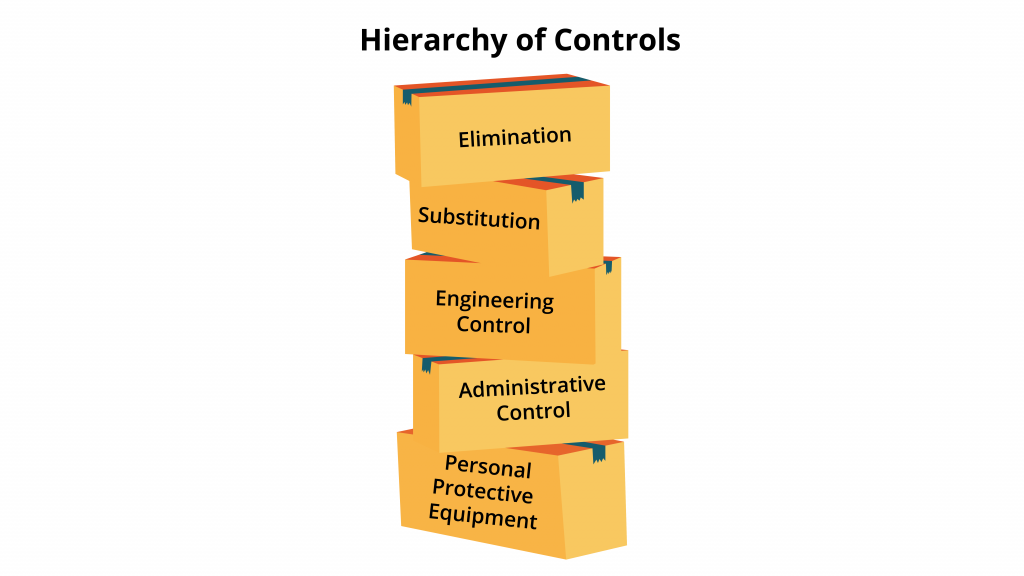
- Choose the most suitable hazard control measures based on the risk assessment. Consider the following hierarchy of controls:
- Elimination: Remove the hazard entirely if possible.
- Substitution: Replace the hazard with a less dangerous alternative.
- Engineering Controls: Implement physical changes or technology to isolate employees from the hazard.
- Administrative Controls: Implement policies, procedures, and work practices to reduce exposure to the hazard.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Use PPE to protect employees when other controls are not feasible or as an additional measure.
4. Develop an Implementation Plan:
- Create a detailed plan that outlines how and when each control measure will be implemented. Assign responsibilities and establish timelines.
5. Communicate and Train:
- Inform employees about the hazard controls and the reasons for their implementation. Ensure that employees receive proper training on the use of controls and safe work practices.
6. Evaluate Effectiveness:
- Continuously monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of hazard controls. Regularly assess whether the controls are reducing or eliminating the identified hazards and associated risks.
7. Adjust and Improve:
- If hazard controls are found to be ineffective or if new hazards arise, adjust the control measures accordingly. Continuous improvement is essential for maintaining a safe workplace.
8. Recordkeeping and Documentation:
- Maintain detailed records of hazard assessments, risk assessments, control measures, training, inspections, and incident reports. Documentation helps track progress and compliance.
9. Involve Employees:
- Involve employees in the hazard control process. Encourage them to report hazards, provide feedback on control measures, and participate in safety committees or teams.
10. Regulatory Compliance:
